BNB Price defined

What Is Binance Coin (BNB)?
Binance Coin (BNB) is the native asset of the Binance ecosystem, primarily used to pay on-chain transaction fees (known as gas, which refers to the required fees for executing transactions and smart contracts on a blockchain) and various service fees within the ecosystem. In certain scenarios, BNB holders can also enjoy trading fee discounts. BNB follows a fixed supply model and features a burn mechanism, meaning that a portion of tokens are permanently removed from circulation to reduce the total supply.
BNB was originally issued as an ERC-20 token on Ethereum before migrating to the BNB Chain (typically referring to a network including BNB Smart Chain and related chains). The maximum supply is capped at 200 million coins, with quarterly burns based on ecosystem trading volume, aiming to gradually reduce the total supply to 100 million. For users, BNB serves a dual purpose as both "network fuel" and a "store of value."
What Are the Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of Binance Coin (BNB)?
As of 2026-01-27:
- Latest Price: $885.20
- Circulating Supply: 136,360,379.49 BNB (refers to the quantity available for trading in the market)
- Total Supply: 136,360,379.49 BNB; Maximum Supply: 200,000,000 BNB
- Circulating Market Cap: ~$120,706,207,924.55 (Market Cap = Price × Circulating Supply)
- Fully Diluted Market Cap: ~$120,706,207,924.55 (theoretical market cap based on maximum or total supply)
- Market Cap Share: ~3.83%
- Price Change: 1 hour +0.22%, 24 hours +1.43%, 7 days -4.72%, 30 days +5.12%
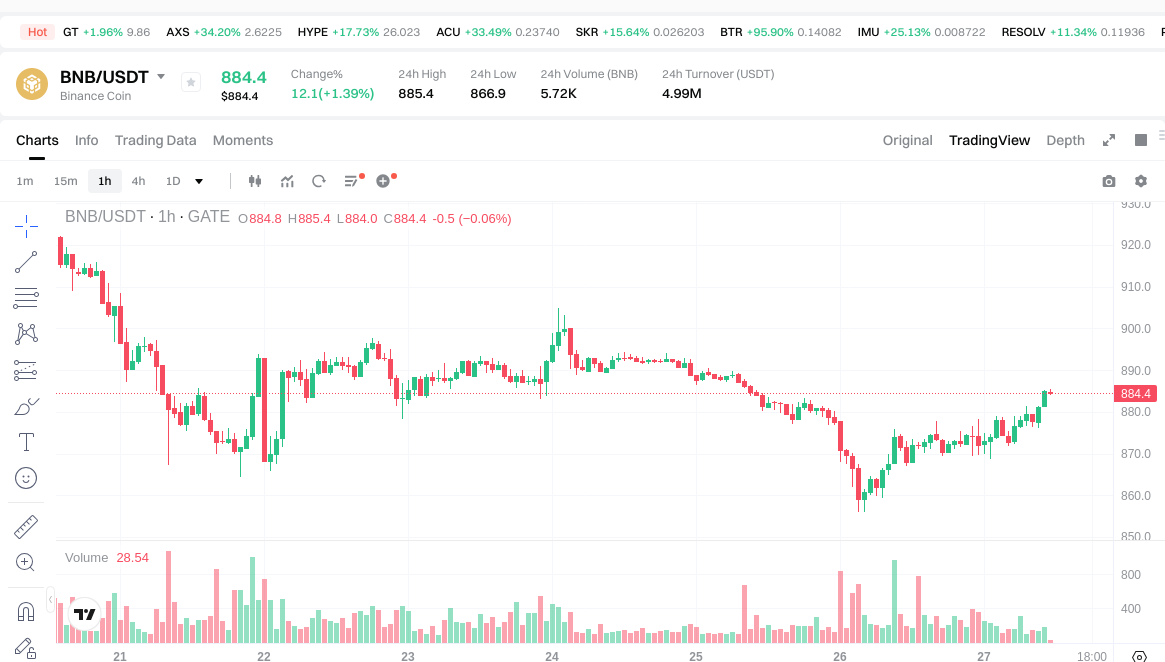
Click to view BNB USDT Price
- 24-Hour Trading Volume: ~$5,006,755.59
These figures reflect short-term volatility and scale, providing a snapshot of BNB's price and market cap trends for fundamental analysis.
Who Created Binance Coin (BNB) and When?
BNB was launched by Binance on July 25, 2017, designed as a general settlement and fee token within its ecosystem. Initially circulating as a token on Ethereum, BNB later migrated to its own network (BNB Chain) to support higher throughput and lower transaction costs. Since inception, BNB has maintained a regular token burn strategy—records are publicly accessible—with the long-term goal of reducing its total supply to 100 million coins.
This evolution transformed BNB from an "exchange ecosystem token" into a "native public blockchain asset," now supporting a broader range of on-chain applications.
How Does Binance Coin (BNB) Work?
On the BNB Chain, BNB is used as gas to pay transaction fees when users transfer funds or interact with smart contracts. Smart contracts are programmable code on-chain that automatically execute agreed logic.
BNB Chain typically utilizes a staking-based consensus mechanism, where validators maintain network security and produce blocks. Staking involves locking assets to participate in network security or governance in exchange for rewards. To control supply, BNB implements periodic token burns that decrease the overall supply and help manage long-term inflation.
Additionally, BNB Chain is EVM-compatible (Ethereum Virtual Machine), enabling developers to deploy applications using familiar tools and languages.
What Can Binance Coin (BNB) Be Used For?
- Paying gas fees for on-chain transfers and smart contract executions.
- Discounting transaction fees and service costs within the ecosystem to enhance cost efficiency.
- Participating in on-chain applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi—lending, swaps, yield aggregators) and NFT marketplaces; BNB can be used for staking, collateralization, or as a denominating asset.
- Facilitating cross-chain transactions and payments by acting as a fee asset or medium of value transfer across different networks and applications.
What Wallets and Extensions Support Binance Coin (BNB)?
Common wallets include browser extensions, mobile apps, and hardware wallets:
- Browser extension wallets are usually EVM-compatible and ideal for connecting to DeFi or NFT applications.
- Mobile wallets offer convenient sending, receiving, and QR code payments.
- Hardware wallets store private keys offline—best suited for long-term custody of significant holdings.
Users must ensure they select the correct network and address standards: BNB Chain commonly uses the BEP20 standard (EVM-compatible); always match network and address formats when withdrawing or transferring funds. Legacy BEP2 networks may require a Memo (note); BEP20 generally does not. A block explorer can help track transaction status and address balances. Mnemonic phrases are backup word sequences for wallet recovery—always store them offline securely.
What Are the Major Risks and Regulatory Considerations for Binance Coin (BNB)?
Market Volatility Risk: Crypto asset prices are influenced by supply-demand dynamics and macroeconomic conditions; short-term price swings can be significant.
Ecosystem Dependency & Technical Risk: The value of BNB depends on the activity of the BNB Chain and its applications; smart contracts may have vulnerabilities or be subject to attacks.
Regulatory & Compliance Uncertainty: Crypto regulations vary globally and may affect certain use cases or liquidity.
Custody & Private Key Security: Storing assets on exchanges poses custodial risks; self-custody requires careful management of private keys or mnemonic phrases to prevent loss or theft.
Network & Fee Risks: Network congestion may lead to higher fees and delayed confirmations—monitor network conditions and fee settings accordingly.
How Do I Buy and Safely Store Binance Coin (BNB) on Gate?
Step 1: Register a Gate account and complete identity verification (KYC), then enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for enhanced account security.
Step 2: Deposit funds. You can purchase USDT via fiat channels or transfer USDT/crypto from another wallet into your Gate account for converting to BNB. USDT is a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, commonly used for trading.
Step 3: Spot trading. Navigate to "Crypto-to-Crypto Trading," select the BNB/USDT market, and buy BNB using either limit orders (set your own price) or market orders (execute at current market price).
Step 4: Withdraw to a self-custody wallet. Go to the "Withdrawal" page, choose BEP20 (BNB Smart Chain) as your network, then paste your wallet address. It is recommended to test with a small amount first before withdrawing larger sums. If using legacy BEP2 network, follow instructions to enter a Memo; BEP20 withdrawals typically do not require Memo.
Step 5: Secure storage & risk control. Back up your mnemonic phrase and private key offline; consider hardware wallets for added safety; enable address whitelisting and withdrawal protection; manage large funds in separate accounts; regularly review wallet security settings.
What Are the Key Differences Between Binance Coin (BNB) and Ethereum (ETH)?
Purpose & Role: BNB acts as both fuel and settlement asset for the BNB Chain ecosystem; ETH is Ethereum’s native asset powering its universal smart contract platform.
Supply & Burn Mechanisms: BNB has a maximum supply (200 million) with periodic burns to reduce circulation; ETH has no fixed cap but uses fee burning and dynamic issuance to impact net inflation.
Network & Fees: BNB Chain focuses on lower fees and higher throughput; Ethereum prioritizes decentralization and security—fees and speed depend on mainnet load and scaling solutions.
Decentralization & Security Model: Both use staking-based consensus mechanisms. Ethereum’s validator set and governance are more decentralized; BNB Chain’s structure reflects its specific ecosystem design.
Compatibility & Development: Both are EVM-compatible, allowing easy migration of applications between chains; however, tooling ecosystems and community support differ.
Binance Coin (BNB) Summary
BNB is the core asset of the BNB Chain ecosystem, serving dual roles as network fuel and value carrier. Its fixed supply with regular burn events aims for long-term supply control. On the application layer, BNB pays on-chain fees, provides fee discounts, and participates in DeFi, NFTs, and other use cases. When investing or using BNB, monitor price trends, market cap changes, burn schedule, ecosystem activity, and regulatory environment; after purchasing via Gate, opt for BEP20 withdrawals and ensure robust security management for private keys and mnemonic phrases—balancing convenience with risk control.
FAQ
Where Can I Check Real-Time Prices for BNB?
You can view real-time BNB prices on major crypto exchanges like Gate, which display up-to-date rates against USD, CNY, and other fiat currencies. You may also consult professional market data sites like CoinMarketCap or CoinGecko that aggregate prices from global exchanges for comprehensive market insights. Compare across multiple sources for the most accurate information.
Does BNB Have Large Price Swings? What Factors Influence Its Price?
BNB experiences typical market volatility that is moderate by crypto standards. Key factors include Binance ecosystem growth milestones, scheduled token burns, overall crypto market sentiment, and changes in macroeconomic policy. When Binance launches new features or conducts major burns, prices often rise; conversely, panic in the broader market can cause declines. Stay updated with official Binance announcements and market news for informed investment decisions.
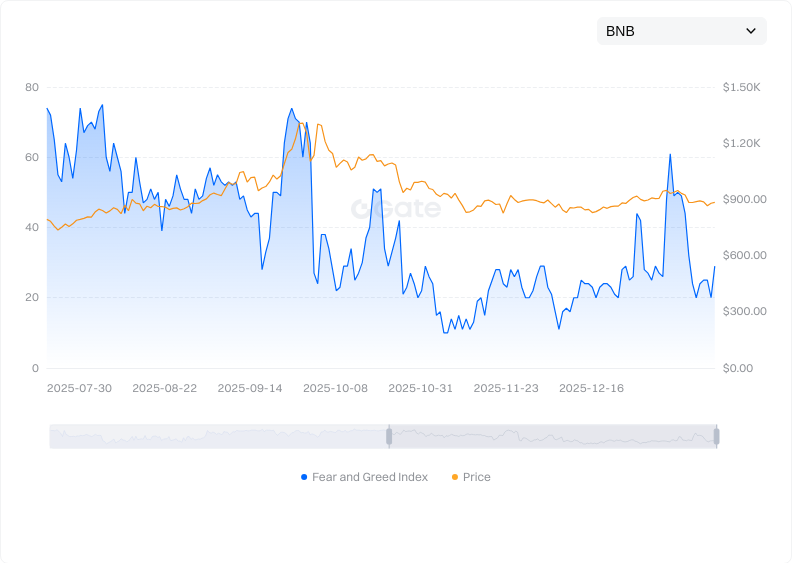
Click to view BNB Fear & Greed Index
Is There a Connection Between BNB’s Price and Binance Exchange Trading Volume?
Yes—the performance of Binance Exchange directly impacts BNB’s price. Higher trading volumes signal greater ecosystem activity and increase demand for BNB, supporting upward price movement.
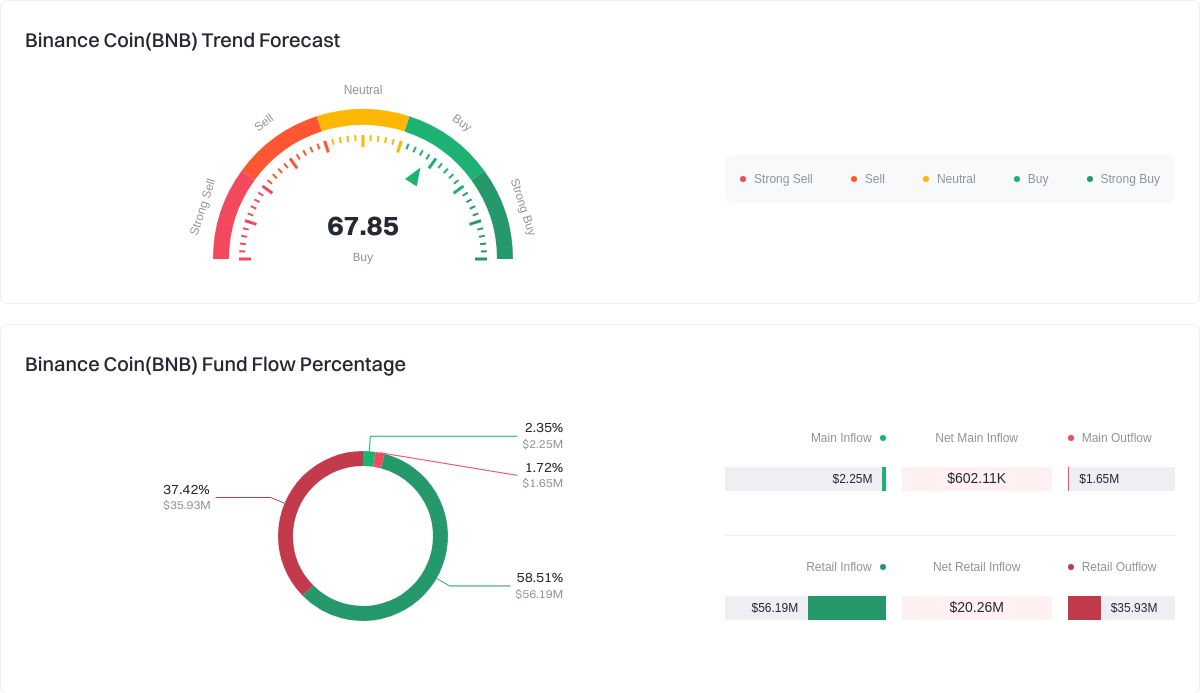
Click to view BNB Fund Flow Share
BNB can be used to pay trading fees on Binance, participate in Launchpad events, etc.—the more diverse its use cases become, the stronger its value proposition. Tracking Binance ecosystem growth and trading volume data helps you understand long-term price trends for BNB.
How Does BNB’s Price Relate to Other Major Cryptos Like BTC or ETH?
BNB generally shows positive correlation with leading cryptos like BTC and ETH—when markets rise, BNB usually rises too; when markets fall, BNB is also affected. However, as an ecosystem token, its fundamentals are more closely tied to Binance’s growth trajectory and may sometimes decouple from broader market trends. For example, if Binance announces major positive developments even during BTC or ETH downturns, BNB may outperform—demonstrating unique value drivers.
At What Price Should I Buy BNB?
This is an investment decision that depends on your risk tolerance and objectives. It’s important to understand BNB’s fundamentals (Binance ecosystem health, burn mechanism), set reasonable target entry ranges rather than chasing short-term highs. You might use dollar-cost averaging or stagger purchases during market corrections. Regardless of timing, prioritize secure asset storage—consider hardware wallets or Gate’s secure storage options.
Glossary of Key Terms Related to BNB
- Binance Smart Chain: The primary platform for BNB utility—supports smart contracts and DeFi ecosystem development.
- Gas Fees: Fees paid in BNB for transactions or contract execution on Binance Smart Chain.
- Staking Mining: Users lock up their BNB to earn rewards or participate in network validation—a main method for yield generation.
- Cross-Chain Bridging: Technology enabling transfers of BNB or other assets across different blockchains—expanding ecosystem interoperability.
- DeFi Ecosystem: Decentralized finance applications built on Binance Smart Chain—including lending protocols, trading platforms, liquidity mining.
- Token Burning: Binance regularly burns a portion of BNB to reduce circulating supply—implementing a deflationary mechanism.
Reference & Further Reading on BNB
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Development / Documentation:
-
Media / Research:
Related Articles

Gate Alpha Launches Points System: Trade On-Chain, Earn Points, Unlock Airdrops

Dogecoin Nears Critical Breakout Window as Market Tensions Build
