Algorand (ALGO)

What Is Algorand?
Algorand is the English name for the blockchain known as 阿拉贡 in Chinese, with ALGO as its native token. As a Layer-1 public blockchain, Algorand aims to accelerate, stabilize, and reduce the costs of global transactions, asset issuance, and decentralized application (dApp) operations by utilizing a highly efficient consensus mechanism.
Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of Algorand (ALGO)
As of 2025-12-29 (user-supplied data), ALGO is priced at approximately $0.120870. Its circulating supply stands at 8,835,932,061.291159 ALGO, with a total supply of 8,836,242,779.738249 ALGO and a maximum supply of 10,000,000,000 ALGO. The circulating market cap is about $1,068,036,664.786962, which is also its fully diluted market cap and represents around 0.032% of the market. Recent price fluctuations include: -0.74% (1 hour), -0.42% (24 hours), +8.59% (7 days), and -14.64% (30 days). The 24-hour trading volume is roughly $402,784.672816.
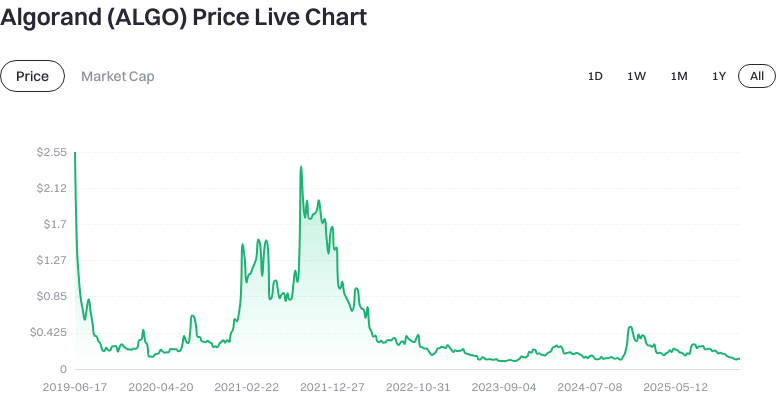
View the latest ALGO price trends
The above data reflects recent volatility and short- to medium-term trends. It is for general reference only; always consult long-term charts and fundamental information before investing.
Who Founded Algorand (ALGO) and When?
Algorand was developed by a team led by MIT professor and Turing Award laureate Silvio Micali. The mainnet launched on 2019-06-16. The project secured about $4 million in seed funding from investors including Pillar and Union Square Ventures. With a strong focus on efficient and decentralized consensus design, Algorand has gradually expanded support for smart contracts and asset issuance, forming an active community driven by its foundation and ecosystem developers.
How Does Algorand (ALGO) Work?
The “consensus mechanism” defines how Algorand’s network reaches agreement on transaction records. Algorand uses Pure Proof of Stake (PPoS), where ALGO holders can participate in validation and block production.
At its core is the Verifiable Random Function (VRF), a cryptographic lottery that randomly selects token holders each round to propose and vote on blocks. Selection is provable mathematically, enhancing fairness and security.
For consensus, Algorand implements an optimized Byzantine Agreement protocol called BA*. Byzantine Agreement ensures that distributed nodes reach consensus even in the presence of faults or malicious actors. BA* finalizes blocks quickly through phased voting, achieving “finality”—meaning once a block is confirmed it cannot be reversed—thus reducing user wait times.
On the functional side, Algorand supports smart contracts written in TEAL and its higher-level languages, as well as the ASA (Algorand Standard Assets) standard for tokenizing assets. With low transaction fees and rapid confirmations, Algorand is ideal for payments and high-frequency applications.
What Are the Main Use Cases for Algorand (ALGO)?
ALGO enables fast, low-cost value transfers such as e-commerce settlements or cross-border micropayments with minimal confirmation delays.
Through the ASA standard, businesses or projects can issue on-chain tokenized assets—including loyalty points, tickets, or supply chain certificates—and automate rules via smart contracts.
Stablecoins and settlement applications are common; fast on-chain finality improves reconciliation efficiency. In DeFi, lending protocols, payment gateways, and yield products can be built on Algorand’s smart contracts, while token holders participate in governance voting.
Key Risks and Regulatory Considerations for Algorand (ALGO)
Price Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices are subject to market sentiment and liquidity, leading to significant short-term swings.
Key and Wallet Security: For self-custody, securely store your mnemonic phrase and private key—loss or leakage results in irreversible asset loss. For custodial storage on platforms, enable two-factor authentication and beware of phishing links.
Technical & Upgrade Risks: Protocol upgrades or smart contract vulnerabilities can cause disruptions or losses; monitor official announcements and audit reports.
Compliance & Regulation: Regulatory frameworks for crypto assets differ by region, potentially impacting fiat gateways, tax reporting, and use cases. Always comply with KYC requirements and local laws when using platforms.
Participation & Decentralization: Low participation or uneven node distribution may affect network decentralization and security.
What Drives Algorand’s (ALGO) Long-Term Value?
Algorand’s long-term value depends on whether its combination of consensus efficiency, instant finality, and low fees continues to attract developers and enterprises. PPoS and VRF lower barriers to participation by enabling random selection; smart contracts and ASA provide infrastructure for payments, settlement, and asset digitization. If real-world adoption grows while maintaining security and stable upgrades, ALGO’s network value could strengthen.
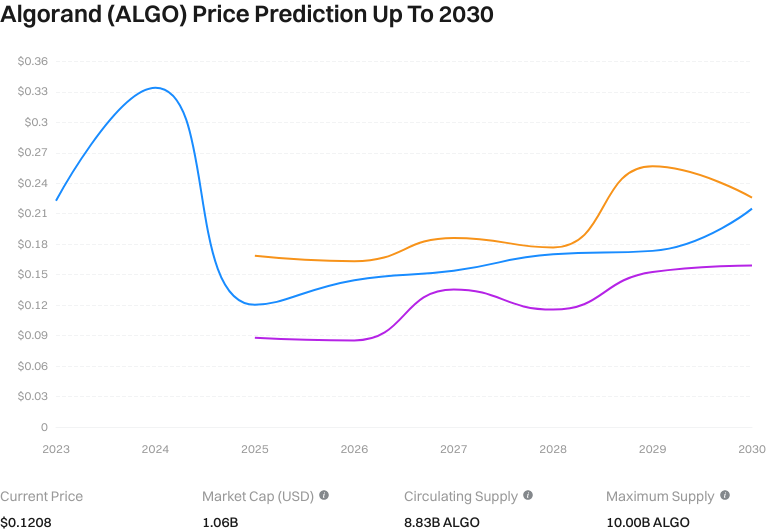
View the ALGO price prediction
How to Buy and Securely Store Algorand (ALGO) on Gate
Step 1: Register and log in to your Gate account. Complete identity verification (KYC) and enable two-factor authentication for login and withdrawals.
Step 2: Deposit funds via your account dashboard. You can buy USDT through Gate’s fiat channel or purchase ALGO directly (if available), or transfer ALGO from your personal wallet to Gate.
Step 3: Go to spot trading, search “ALGO,” select the ALGO/USDT trading pair, review order books and charts for price and liquidity.
Step 4: Place your order. Use a “market order” for instant execution or a “limit order” to set your desired price; enter the amount and submit.
Step 5: Secure your assets once they arrive. For short-term trading, keep them in your Gate account with withdrawal anti-phishing code enabled; for long-term holding, opt for self-custody using an official or community-supported wallet like Pera Wallet—create a new address and back up your mnemonic phrase securely.
Step 6: Withdraw to your self-custody wallet. On Gate’s withdrawal page, enter your Algorand address, confirm network details, amount, and fees; test with a small withdrawal before transferring large sums.
Step 7: Safely store backups and periodically review security. Keep mnemonic phrases offline in multiple locations; consider hardware wallets for enhanced security; regularly check addresses and transaction records; watch out for suspicious links or fake support contacts.
Risk Reminder: Always verify chain type and address format before withdrawal; never share your private key—even in response to “airdrop” offers or customer support requests.
How Does Algorand (ALGO) Compare to Cardano?
Consensus Mechanism: Algorand uses PPoS with VRF-based random selection and BA* finality; Cardano employs the Ouroboros PoS family with slot-based elections. Both prioritize efficiency and security but follow different technical paths.
Smart Contracts & Languages: Algorand features TEAL and its high-level languages focused on simplicity and safety; Cardano uses Plutus (based on Haskell) emphasizing formal verification and expressiveness. Choice depends on team skills and project needs.
Performance & Finality: Algorand offers rapid finality with low fees—ideal for payments and high-frequency use; Cardano continues to iterate scalability with sidechains and extensions. Actual performance depends on network state and implementation.
Tokens & Supply: ALGO has a maximum supply of 10 billion used for consensus participation and fees; ADA is also staked and used for fees but features different issuance schedules. Each network has distinct economic models and governance structures.
Ecosystem Focus: Algorand targets payments, asset issuance, and enterprise applications; Cardano leans toward academic rigor with gradual feature rollouts. Both are expanding in DeFi, stablecoins, and public projects.
Summary of Algorand (ALGO)
Algorand (阿拉贡, ALGO) is a high-performance Layer-1 blockchain utilizing PPoS, VRF random selection, and BA* consensus to deliver fast finality at low cost with support for smart contracts and asset issuance. The current market data shows a clear structure for market cap and supply but also highlights risks such as price volatility as well as technical and regulatory challenges. For regular users, Gate offers a step-by-step process for registration, purchase, withdrawal, and secure self-custody of private keys. For developers and enterprises, Algorand’s value grows as real-world adoption increases in payments, settlement, or tokenization scenarios. Users are advised to understand consensus mechanisms and wallet safety while aligning participation with their needs and risk tolerance.
FAQ
What Are the Main Differences Between Algorand and Cardano?
Both are third-generation public blockchains but differ in their consensus mechanisms. Algorand adopts Pure Proof of Stake (PPoS) with fast block confirmations (4.5 seconds), while Cardano uses the Ouroboros mechanism focusing on academic rigor. Algorand offers lower transaction costs suitable for high-frequency trading; Cardano’s ecosystem is still developing. Both are strong projects—choose based on your use case.
How Do Algorand’s Transaction Speed and Costs Compare to Bitcoin & Ethereum?
Algorand is significantly faster than both Bitcoin and Ethereum. Average confirmation time is 4.5 seconds versus Bitcoin’s 10 minutes or Ethereum’s 12–15 seconds. Transaction fees are about $0.001 per transfer—hundreds of times cheaper than Ethereum—making Algorand ideal for micropayments and high-frequency transactions.
What Role Does ALGO Play in the Algorand Network?
ALGO is Algorand’s native token with three main functions: holders can participate in network validation to earn rewards (staking); pay transaction fees; and vote in network governance decisions. In short, ALGO powers network operations and incentivizes participants.
How Do You Stake ALGO to Earn Rewards?
Staking on Algorand is straightforward. Purchase ALGO via Gate or any supported platform then transfer it to a staking-enabled wallet such as the official Pera Wallet. Enable Participation in the wallet settings; your ALGO will automatically participate in consensus to earn rewards—no minimum holding required. Tokens remain under your control throughout staking with the option to unstake at any time.
How Is Network Security Maintained on Algorand?
Algorand ensures security through its Pure Proof of Stake mechanism which randomly selects validators—making it difficult for attackers to predict or control nodes. Cryptographic proofs guarantee that once a block is finalized it cannot be reversed. Additionally, the core team includes cryptography experts such as Silvio Micali; designs undergo extensive academic review.
Quick Reference Glossary for Algorand (ALGO)
- Pure Proof of Stake: The consensus mechanism used by Algorand, enabling validation based on token holdings without requiring high-performance hardware.
- AVM (Algorand Virtual Machine): Executes smart contracts written in TEAL.
- Atomic Swap: Trustless cross-asset transactions on Algorand ensuring atomicity and security.
- Staking: Process where ALGO holders earn rewards by participating in network validation—the core of PPoS.
- Smart Contract: Self-executing code running on the Algorand blockchain enabling complex logic.
- Finality: Once an Algorand transaction is confirmed it cannot be reversed, guaranteeing instant finality.
Further Reading & References
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Developer Resources / Docs:
-
Trusted News / Research:
Related Articles

AltLayer Explanation: Aggregation as a Service

What Are Altcoins?
